本文分析ThreadLocal的原理和使用
1.ThreadLocal简介
多线程访问共享变量时容易出现并发问题,为了保证线程安全,一般会给共享变量进行适当的加锁同步。如果不想加锁呢? ThreadLocal可以做到线程隔离,多个线程访问共享变量时,访问的是自己线程的变量。 ThreadLocal提供了线程本地变量,如果创建了一个ThreadLocal变量,那么访问这个变量的每个线程都会有这个变量的一个本地副本,当多线程操作这个变量时,实际操作的是自己本地内存的变量,从而避免线程安全的问题。
2.ThreadLocal使用
public class ThreadLocalDemo {
static ThreadLocal<String> stringThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<String>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
stringThreadLocal.set(Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println(stringThreadLocal.get());
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
},"i am thread --"+i);
thread.start();
}
}
}
运行结果

3.ThreadLocal的原理
Thread类中有两个包访问变量,一个是threadLocals ,一个是inheritableThreadLocals,它们都是ThreadLocalMap类型的变量。
 而ThreadLocalMap又是ThreadLocal的内部类。
默认情况下,每个线程的这两个变量都为null,只有当线程第一次调用ThreadLocal 的set 或者get方法时才会创建他们。
每个线程的本地变量是存在调用线程的threadLocals变量中的,ThreadLocal通过set方法把value放在调用线程的threadLocals变量中,通过get方法取出调用线程的threadLocals中的值。
Thread里面的threadLocals为何设计为map结构?因为每个线程可以关联多个ThreadLocal变量。
而ThreadLocalMap又是ThreadLocal的内部类。
默认情况下,每个线程的这两个变量都为null,只有当线程第一次调用ThreadLocal 的set 或者get方法时才会创建他们。
每个线程的本地变量是存在调用线程的threadLocals变量中的,ThreadLocal通过set方法把value放在调用线程的threadLocals变量中,通过get方法取出调用线程的threadLocals中的值。
Thread里面的threadLocals为何设计为map结构?因为每个线程可以关联多个ThreadLocal变量。
下面分析下 ThreadLocal 的set、get及remove方法 1.set
public void set(T value) {
//获取当前调用线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
//将当前线程作为key 去查对应的线程变量threadLocals
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
//当前线程的threadLocals不为null
if (map != null)
//将当前ThreadLocal 对象作为key传入map
map.set(this, value);
else
//创建map
createMap(t, value);
}
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
//当前线程的threadLocals 赋值 以当前ThreadLocal 对象作为key 创建的ThreadLocalMap
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
//ThreadLocalMap的构造函数
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {
//Entry为ThreadLocalMap的内部类 INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
//计算应该存放的位置 i 因INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16 相当于对 16 取余
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);
//存放到table[i]
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);
size = 1;
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
2.get
public T get() {
//获取当前调用线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
//将当前线程作为key 去查对应的线程变量threadLocals
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
//以当前ThreadLocal对象作为key 去取 map中的 entry
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
private T setInitialValue() {
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
remove
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
//拿到table数组
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
//找到在数组中存放的位置 i
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
//判断key是否相等
if (e.get() == key) {
//清除
e.clear();
expungeStaleEntry(i);
return;
}
}
}
ThreadLocalMap内部类 Enrtry
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
Enrtry 继承自软引用,当对应的ThreadLocal对象为null时,此Entry对象会被JVM回收,避免出现内存泄漏。
4.ThreadLocal不支持继承性
public class TestThreadLocal {
public static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<String>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
threadLocal.set("hello");
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("sub thread: " + threadLocal.get());
}
}).start();
System.out.println("main: "+ threadLocal.get());
}
}
 也就是说,同一个ThreadLocal变量在父线程中被设置值后,在子线程中是获取不到的。
也就是说,同一个ThreadLocal变量在父线程中被设置值后,在子线程中是获取不到的。
5.InheritableThreadLocal类
利用InheritableThreadLocal类,子线程可以访问父线程中的本地变量。
//继承ThreadLocal类
public class InheritableThreadLocal<T> extends ThreadLocal<T> {
protected T childValue(T parentValue) {
return parentValue;
}
//返回当前线程的inheritableThreadLocals变量
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.inheritableThreadLocals;
}
//初始化当前线程的inheritableThreadLocals变量
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.inheritableThreadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
}
当子线程初始化时会判断父线程的inheritableThreadLocals变量是否为null,不为null 则会赋值给子线程inheritableThreadLocals变量
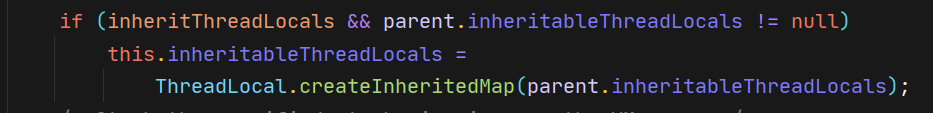
static ThreadLocalMap createInheritedMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {
//这个构造函数 仅此方法createInheritedMap调用
return new ThreadLocalMap(parentMap);
}
private ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {
Entry[] parentTable = parentMap.table;
int len = parentTable.length;
setThreshold(len);
table = new Entry[len];
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
Entry e = parentTable[j];
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
ThreadLocal<Object> key = (ThreadLocal<Object>) e.get();
if (key != null) {
//这里调用InheritableThreadLocal类覆盖的 childValue方法
Object value = key.childValue(e.value);
Entry c = new Entry(key, value);
int h = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
while (table[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, len);
table[h] = c;
size++;
}
}
}
}
改为InheritableThreadLocal 运行
public class TestInheritableThreadLocal {
public static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
threadLocal.set("hello");
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("sub thread: " + threadLocal.get());
}
}).start();
System.out.println("main: "+ threadLocal.get());
}
}

「真诚赞赏,手留余香」
真诚赞赏,手留余香
使用微信扫描二维码完成支付
